Business structuring is the foremost key decision to be made when establishing any business. It lays the foundation for the business in terms of taxation and ownership. So, be careful what you choose to get the best outcomes.
What is Business Structuring?
Business structure is the legal structure based on which it is registered and will function. Also known as the ownership structure of the company and legal structure, it defines what the business can do and what it can’t on the operational and financial front.
Simply put, business structure defines three main aspects,
- Ownership – Who owns it, what percentage, etc.
- Liability – Are the owners/shareholders personally liable to its operations and debts?
- Taxation – Taxes are vastly based on the business structure.
Structuring doesn’t end here. There are other aspects like corporate structuring and financial structuring that are part of the business framework.
4 Major Types of Business Structures
There are many business structures available depending on the jurisdiction you wish to set up the business. But all of them will fall under the following 4 major categories,
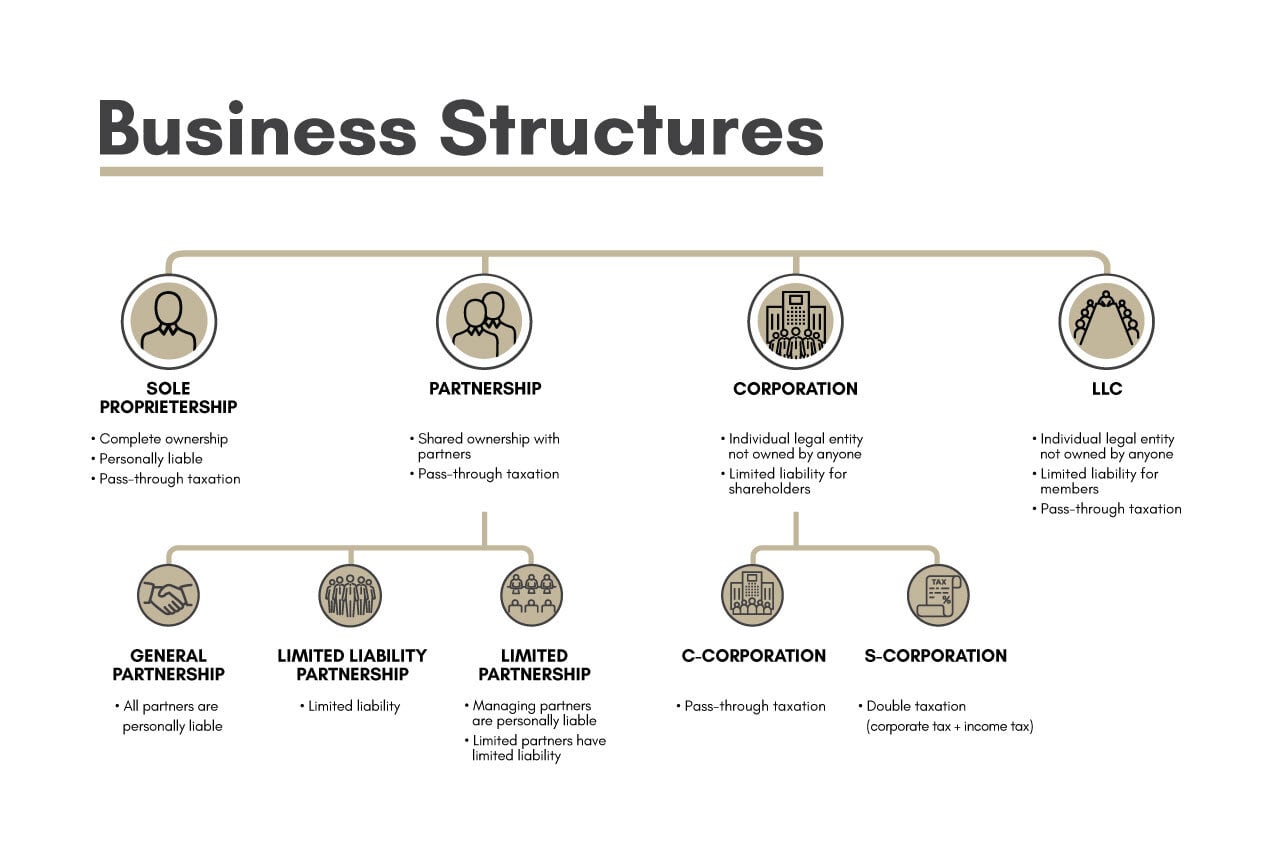
Sole proprietorship
The simplest business structure of all is the sole proprietorship. The business or the company registered under sole proprietorship is considered an extension of the person. The taxation also is carried the same way. The profits and loss of the business are to be reflected as income in the owner’s income tax report. This kind of establishment is termed flow-through entity or pass-through entity.
Proprietorship eliminates the problem of double taxing which occurs in other complex business structures. The complete operational power is vested with the owner. It is also the easiest to set up and maintain for a small business.
The downsides come in the form of liability. The owner is personally liable for the losses and decisions they make for the business. However sole proprietorship is the most convenient for a family-run business, one-man consulting firms and most small-scale businesses.
- Ownership – Complete ownership by a single person.
- Liability – Personally liable to all the obligations and debts of the company.
- Taxing structure – The profit and loss of the business are directly taken as owners’ income.
ADVANTAGES
- Easiest to setup
- Easy to operate and maintain
- No business tax on profit. (only income tax)
DISADVANTAGES
- Personal liability.
Who should opt for a Sole Proprietorship Business Structure?
Home businesses, one-person consulting, a small business that doesn’t require capital rising or has the fear of liability.
Partnership
The partnership is the simplest method of setting up a company when more than one people are involved. It is similar to a sole proprietorship in terms of taxation but here two or more people form a relation between themselves through a partnership deed before setting up the business. (might vary with jurisdiction)
- Ownership – Owned by the partners.
- Liability – Liable to debts, obligations and decisions of the partners. (with some exceptions)
- Taxation – Pass-through taxing split between partners of the business.
The Liability and control over the business vary with the nature of the partnership – limited or general partner. A general partner has control over the business operation and is personally liable to the debts and obligations. Whereas a limited partner puts in the capital and has limited liability (often known as a silent partner).
Types of partnership
- General partnership: All the partners share the liability and responsibility of the business based on the shareholding.
- Limited Liability Partnership: All of the partners are limited partners with limited liability. Here all the partners are involved in the operation usually by electing a board of members.
- Limited partnership: It is where at least one of the partners is a general partner and the rest are passive partners who are limited by liability and can’t take part in the management.
ADVANTAGES
- Easier to set up and operate among other multi-owner business structures
- No business tax on profit. (only income tax)
DISADVANTAGES
- Personal liability (with some exemptions)
Who should opt for a Partnership Business Structure?
Partners looking for a basic business setup without the feasibility of capital raising.
Corporation
A corporation is a separate entity that is treated as an individual in terms of liability and taxing. A complex business structure to set up but has significant upsides to it. Usually suitable for large scale business, the corporation has double taxing.
Double taxing is the term used to mention the two levels of taxation the profit from a business goes through. First is the corporate income tax that is to be paid by the corporation for the profit made. The second is on the dividends passed over to the shareholders that are taxed in the share holders’ income tax.
While that is one significant downside the liability is a major plus or the lack thereof. The shareholders of the company are not liable to the corporation’s debts and claims. Those need to be settled with the corporations’ assets considering the corporation as a standalone entity leaving out the personal assets of the shareholders.
Shareholders get voting rights based on which a board is formed and operations are handled, usually. The positives don’t stop there. The company can retain a certain amount with itself without taxing or distributing it to shareholders.
A corporation can also sell shares to public or preferred buyers to raise capital for the operation and expansion of the corporation.
- Ownership – There is no owner to a corporation. The corporation is an independent entity with shareholders.
- Liability – Shareholders are not personally liable for the debt and obligations of the corporation.
- Taxation – Double taxing (Corporate income tax + individual’s income tax)
Types of corporation
- C-Corporation: The usual corporation with no limits on the number of shareholders and double taxing
- S-Corporation: It is a special type of corporation available in the USA and few other countries where up to 100 shareholders are allowed to form a corporation with pass-through entity taxation. A hybrid of partnership and corporation business structure with some limitations and strict guidelines to set up.
ADVANTAGES
- Limited liability on debts and obligations for shareholders
- Can raise capital by selling shares
DISADVANTAGES
- Double taxation
- Complex to set up and run corporate business structure
Who should opt for Corporation Business Structure?
Large scale businesses that require all the flexibility of a corporation and your industry & jurisdiction allows for LLC registration.
Other Business Structures
Apart from the major categories there are some less known and less opted business structures.
B Corporation
B means ‘Benefit Corporation’. Allowed for companies with special good will in terms of climate change and other societal benefits. It is the same as C-Corporation except for some tax benefits.
Non-Profit Corporation
As the name explains these are Corporations formed and run without profit motive like charity organizations, educational institutions and research institutes. They operate and administer similar to C-Corporation but are exempt from all of the business level taxes.
Closed corporation
C-Corporation with pre-determined shareholders. Capital rising is not feasible without changing the business structure.
Open Corporation
C-Corporation that is available for the public to buy and sell shares.
Joint Venture
Two or more legal entities entering into partnership for a limited time span. It is similar to partnership in terms of taxation, ownership and liability
Cooperative
It is basically a corporation that serves the owners itself. Which means the owner and the end consumer are the same.
FAQs
Can you change from one business structure to other?
Yes, you can change from one structure to another but the process is going to be complex. Consult an attorney or a corporate structuring expert.
Can I transfer your business across the country/state? (jurisdiction)
Yes, can be done. However, not all jurisdiction allows it. Please check with an expert.
Which business structure is suitable for me?
There are a lot of factors involved in the decision making like goals, needs, jurisdiction, industry, etc., Do an in-depth analysis before choosing the right Business structure.
Is corporate structure the same as business structure?
No corporate structure is different from a business structure. While business structure deals with ownership, liability, taxation and operational guideline’s corporate structure is about the internal classification of teams, departments and so on.
What is financial structuring?
Financial structuring is the optimization of finances – debt, equity, expense and taxes for the best of the company. It is ideal to take financial structuring consulting in the company formation stage.


